Marriage Migrant(F-6)
| Eligible Persons and Scope of Activity | A person whose marriage has been validly established in Korea and who intends to reside in Korea to continue their marital life with a Korean national
A person recognized by the Minister of Justice as the father or mother raising a child born from a marital relationship (including a de facto marital relationship*) with a Korean national * A de facto marital relationship is established when there is a subjective intent to marry and, objectively, a shared life as a married couple that is recognized as such according to societal norms (Supreme Court Case 98Meu961, Dec. 8, 1998). Examples: Mere cohabitation without intent to marry is not recognized as a de facto marriage Relationships resembling bigamy, which are not protected under the law, are not considered de facto marriages A person who had been residing in Korea while married to a Korean national but, due to the death or disappearance of the spouse or other circumstances not attributable to the person, can no longer maintain a normal marital relationship, and is recognized as such by the Minister of Justice |
| Maximum Duration of Stay That Can Be Granted at One Time | 3 years |
| Detailed Subcategories of Residence Status | Code Classification Criteria
F-6-1: A foreigner whose marriage is validly established under the laws of both countries and who intends to reside in Korea to continue married life with a Korean national F-6-2: A parent (father or mother) who, after the termination of a marital relationship (including a de facto marital relationship), is raising or intends to raise a minor child born from that relationship in Korea F-6-3: A person who had been residing in Korea while married to a Korean national, but due to the death or disappearance of the spouse or other circumstances not attributable to the person, is unable to maintain a normal marital relationship |
| Activities Outside the Scope of Residence Status | Not subject to employment restrictions based on the classification of residence status |
| Change or Addition of Workplace | Not applicable |
| Grant of Residence Status | # Article 23 (Grant of Residence Status) of the Immigration Act
A foreign national born in the Republic of Korea who does not qualify for a residence status under Article 10 must obtain a residence status in accordance with Presidential Decree within 90 days from the date of birth. Likewise, a foreign national who stays in Korea and loses or renounces Korean nationality, or who otherwise becomes ineligible for a residence status under Article 10 due to other reasons, must obtain a residence status within 30 days from the date such reason occurs, in accordance with the Presidential Decree. 1. A person who loses Korean nationality while residing in Korea may be granted a Marriage Migrant (F-6) residence status depending on the purpose of stay. 2. Local discharges from the U.S. Forces Korea (USFK) may be granted a Marriage Migrant (F-6) residence status depending on the purpose of stay. ※ Required documents and permitted duration of stay are the same as for residence status change applications. |
| Permission to Change Residence Status (F‑6‑1) | A. Permission to Change Residence Status to Spouse of a Korean National (F‑6‑1)
1. Eligible Applicants * Individuals currently residing legally in Korea who wish to change their status to “Spouse of a Korean National (F‑6‑1).” * Exception: Individuals residing under the “Tourism-Employment (H‑1)” status are **not eligible** for a change to F‑6 under the “Tourism-Employment (H‑1) Visa Issuance and Stay Management Guidelines.” In general, the following are not eligible for status change and must exit Korea and re-enter by obtaining a new visa from a Korean diplomatic mission: 1. Short-term visa holders 2. Illegal residents (including unauthorized entrants and users of forged or altered passports) 3. Individuals granted permission to extend stay for departure (those granted a grace period to depart are not eligible for status change) 4. General criminal offenders (excluding those fined only) 5. Those who, while in any of the above statuses, received an “Other (G‑1)” status *Short-term visa entrants include holders of Visa Waiver (B‑1), Tourist Transit (B‑2), Temporary Coverage (C‑1), and short-term employment (C‑4) visas.* *Exception:* German nationals who entered under Visa Waiver (B‑1) **may** be eligible to change to F‑6. However, if a status change is deemed unavoidable for humanitarian reasons —such as pregnancy, childbirth, or caring for a child born within the marriage (excluding adopted children)—a case-by-case review may allow change within Korea. ([네이버 블로그][1]) 2. Period of Stay Granted: Up to 1 year ([네이버 블로그][2]) 3. Authorized for Approval: Director of the district immigration office (or branch thereof) ([네이버 블로그][2]) 4. Required Documents: Generally based on documentation required for F‑6 visa issuance; additional or reduced documents may be requested during submission and review ([네이버 블로그][2]) B. Permission to Change Residence Status for a Parent Raising a Minor Child (F‑6‑2) 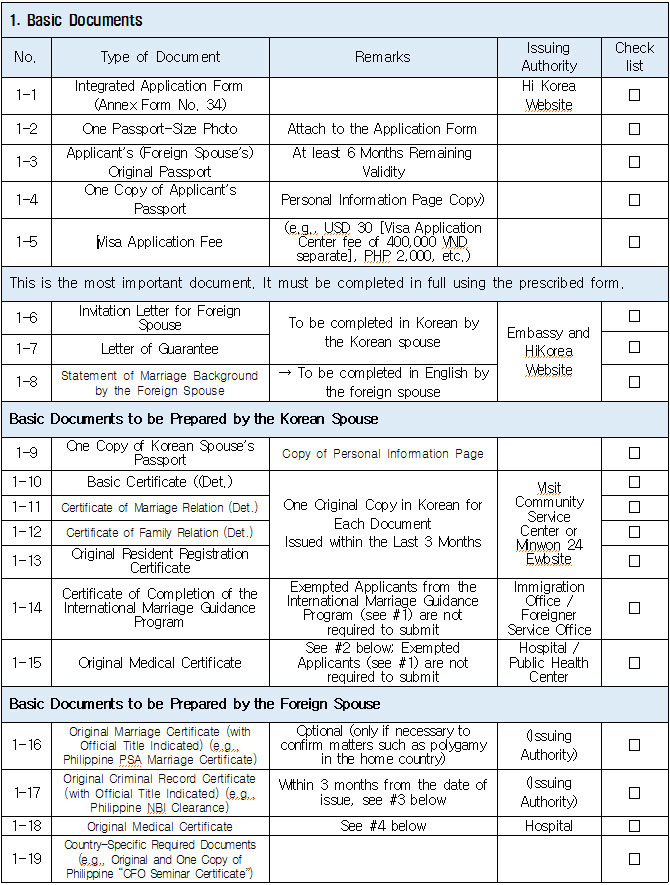 1. Eligible Applicants * Foreigners residing under a status other than F‑6 who are the father or mother raising (or intending to raise) in Korea a minor child born from a marital relationship (including de facto marriage) with a Korean national. 2. Period of Stay Granted : 1 year 3. Required Documents may include: * Application (form No. 34), passport, alien registration card (if applicable), one passport-style photo, and fee * Certificate of basic family registry and family relationship certificate in child’s name (if the child is Korean) * Proof of family (parent–child) relation (e.g., birth certificate or genetic test documentation) * Proof of child‑rearing (e.g., custody court decision, family registry listing the child, confirmation from local community leaders or relatives within the 5th degree in Korea) * Proof of marital termination (e.g., divorce, spouse’s death or disappearance), if applicable * Criminal record certificate and health check (exempt if previously submitted and the applicant hasn’t stayed continuously abroad for 6 months or more) * Other documents deemed necessary by the immigration office C. Permission to Change Status for Individuals Whose Marriage Has Ended (Spouse’s Death, Disappearance, etc.) (F‑6‑3) 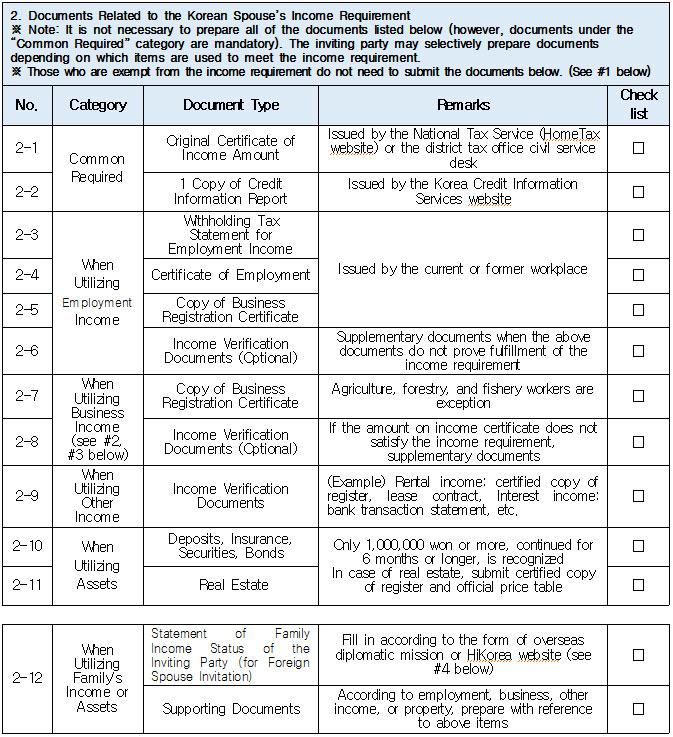 1. Eligible Applicants (must meet all of the below): * Foreigners residing under a status other than F‑6 * Those whose marriage to a Korean national has ended due to death, disappearance, or other reasons not attributable to them, and who cannot maintain a normal marital relationship—**excluding** short-term stayers, criminal offenders (excluding those fined only), and those extended a stay to depart; also excluding those who were in those restricted statuses but were later granted G‑1. * Note : Applicants already residing under F‑6 at the time remain eligible for renewal, not status change. 2. Period of Stay Granted : **1 year** 3. Required Documents include: * Common documents: Application (form No. 34), passport, alien registration card, photo, fee, criminal record, health check (with same exemption criteria as above) * For spouse’s death: death certificate or basic family registry form stating death; document proving marriage * For divorce: marriage registry stating divorce, divorce court documents, proof of fault when applicable (e.g., hospital report, non-prosecution decision, certification by women’s rights group, relative statements, community confirmation) * For disappearance: disappearance ruling documentation; proof of marital relationship * Additional documents may be requested if necessary by immigration authorities 4. Authorized for Approval : Director of the district immigration office D. Permission to Change to Household Affairs (F‑1‑6) for Post‑Marriage Property or Estate Matters 1. Eligible Applicants * Individuals whose marriage to a Korean national has ended, who do not qualify under F‑6‑3, but whose stay in Korea is unavoidable due to property division, estate matters, or similar reasons. 2. Review Criteria & Considerations : Necessity to stay and whether a normal marriage was maintained beforehand 3. Period of Stay Granted : Up to 6 months (the F‑1‑6 status can be granted for up to 1 year from the date of status change) 4. Required Documents : * Application (form No. 34), passport, alien registration card, photo, fee * Guarantee letter (guarantor must be specified) * Marriage registry showing divorce * Documentation explaining why stay is unavoidable (e.g., property division documents) * Additional documents deemed necessary by the immigration office * Proof of residence (e.g., lease contract, employer’s housing certification, notice for approaching stay expiration, utility bills, dorm receipts) * #2 (Other Documents Proving Communication Ability) If either the Korean spouse or the foreign spouse ① submits a language proficiency test score above a certain level, or ② passes an interview conducted in the relevant language at the embassy, they may be recognized as having met the communication requirement. 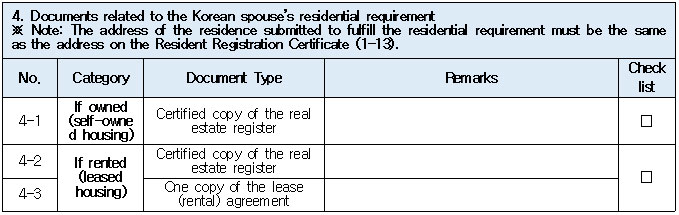 * #1 (Housing Requirement) The residence submitted to meet the housing requirement must be owned or leased under the name of the Korean spouse, or the Korean spouse’s immediate family member, brother, or sister. If the residence is owned or leased under the name of a third party, it is, in principle, considered not to meet the housing requirement. However, exceptions may be made if the residence is deemed acceptable under social norms, such as company-provided housing. 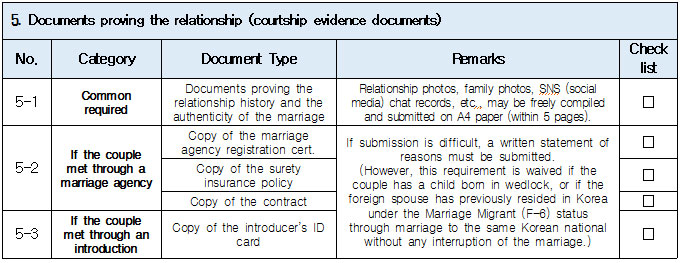 * #1 (Exemption from Submission of Documents Explaining How the Couple Met) ① When the couple has a child born between them, or ② When the foreign spouse has previously stayed in Korea under a Marriage Migrant (F-6) visa, regardless of the length of stay (However, this does not apply if the spouse has changed or if the same marriage was previously dissolved.) [List of Required Documents for Simplified Document Submission by Case] ▢ In the case where the couple has a child born between them – Required Documents List 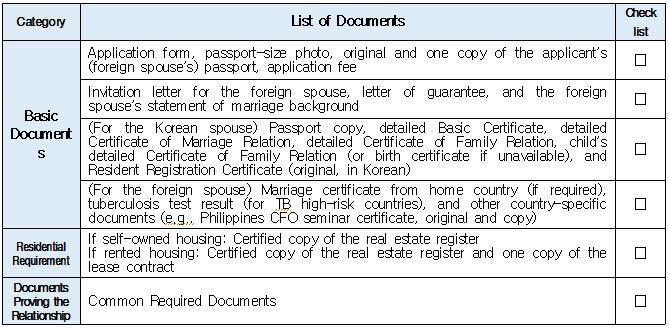 ▢ List of Required Documents for Those Exempt from the International Marriage Guidance Program (e.g., Pregnancy, etc.) (This category also includes those who are fully exempt from submitting the Korean and foreign spouses’ medical examination certificates and criminal record certificates.) 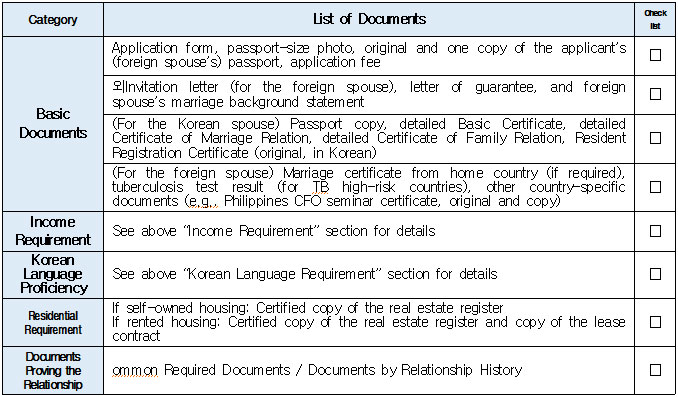 ▢ In the case where the foreign spouse has previously stayed in Korea under a Marriage Migrant (F-6) visa 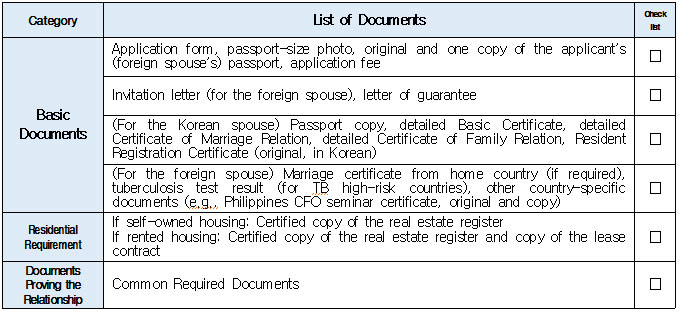 ※ However, this does not apply if the spouse has changed or if the same marriage was previously dissolved. □ Countries not subject to the International Marriage Guidance Program 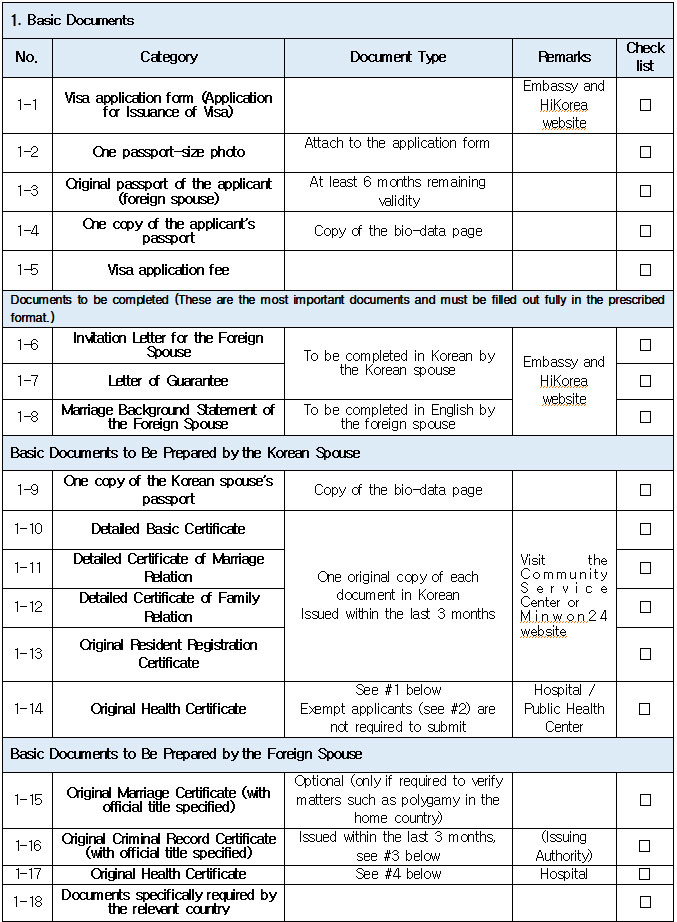 * #1 (Regarding the Korean Spouse’s Medical Examination Certificate) It must be issued by a hospital-level medical institution, public health center, or a designated medical examination institution under Article 3 of the Regulations on Physical Examinations for Public Officials Employment. The certificate must use the Public Official Employment Health Examination Form and be issued within six months prior to the visa application date. * #2 (Exemption from Submission of the Korean Spouse’s Medical Examination Certificate) The following individuals are exempt from submitting the Korean spouse’s medical examination certificate: ① Those who can prove that the Korean and foreign spouses maintained a relationship while the foreign spouse continuously resided for six months or more in the foreign spouse’s country or in a third country under a long-term visa for study, dispatch, or other purposes; ② Those who can prove that the foreign spouse legally resided in Korea for 91 days or more under a long-term stay visa as specified in Annex 1-2 of the Enforcement Decree of the Immigration Control Act, and maintained a relationship with the Korean spouse during that time; ③ Those for whom humanitarian consideration is necessary due to pregnancy, childbirth, or other similar reasons involving either the Korean or the foreign spouse. * #3 (Regarding the Foreign Spouse’s Criminal Record Certificate) If the Korean spouse qualifies for exemption under section #2, the foreign spouse’s criminal record certificate is also exempted from submission. * #4 (Regarding the Foreign Spouse’s Medical Examination Certificate) It must be issued within six months before the visa application date and include the hospital name, address, contact information, and the attending doctor’s signature, and it must be computer-typed. In addition to the standard medical checkup items, the certificate must also include a tuberculosis (TB) test. If the Korean spouse qualifies for exemption under section #2, the foreign spouse’s medical examination certificate is also exempted, but the tuberculosis (TB) test result must still be submitted. (If the applicant is pregnant and unable to undergo a TB test, please contact the relevant authorities separately.) 1. Nepal 2. Timor-Leste 3. Russia 4. Malaysia 5. Mongolia 6. Myanmar 7. Bangladesh 8. Vietnam 9. Sri Lanka 10. Uzbekistan 11. India 12. Indonesia 13. China 14. Cambodia 15. Kyrgyzstan 16. Thailand 17. Pakistan 18. Philippines 19. Laos 20. Kazakhstan 21. Tajikistan 22. Ukraine 23. Azerbaijan 24. Belarus 25. Republic of Moldova 26. Nigeria 27. South Africa 28. Ethiopia 29. Democratic Republic of the Congo 30. Kenya 31. Mozambique 32. Zimbabwe 33. Angola 34. Peru 35. Papua New Guinea 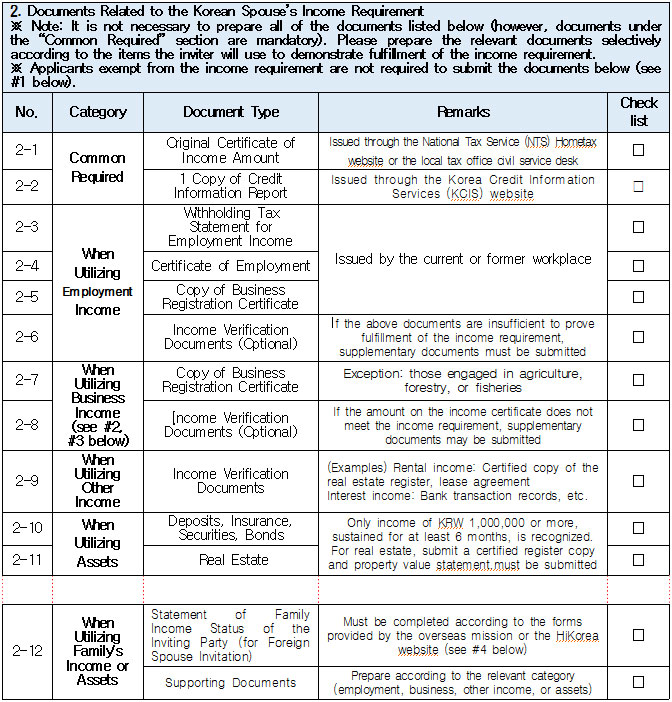 * #1 (Exemption from Income Requirement) ① When the couple has a child born between them; ② When the couple has lived together overseas for at least one year prior to the visa application date and therefore has no domestic income during the past year; ③ When the foreign spouse has previously stayed in Korea under a Marriage Migrant (F-6) visa, regardless of the length of stay (however, this does not apply if the spouse has changed or if the same marriage was previously dissolved). However, those falling under ① must submit a Family Relationship Certificate under the child’s name (or a Birth Certificate if the child was born before marriage and before acquiring Korean nationality), and those falling under ② must submit documents proving cohabitation. * #2 (Notes on Business Income 1) As a rule, business income is determined based on the amount stated in the Income Amount Certificate issued by the National Tax Service. If your actual income is higher than the amount recorded on that certificate, it may be considered as underreporting income. Therefore, you should file a corrected tax return with the tax office and submit the revised Income Amount Certificate. * #3 (Notes on Business Income 2) In principle, income-related documents from one year prior to the date of application must be submitted. However, because business income is reported in May of the following year, if the most recent income stated on the Income Amount Certificate meets the required income threshold and the Korean spouse is still engaged in the same business at the time of application, exceptions may be made even if the income is not exactly from one year prior. (A field investigation may be conducted depending on the circumstances.) * #4 (Scope of Family Members Whose Income Can Supplement the Requirement) Only immediate family members (parents, grandparents, children, etc.) who are registered as residing in the same household with the Korean spouse on the Resident Registration, or the marriage migrant being invited, may supplement the income requirement. (Only income or assets earned within Korea during the past year are recognized.) Even if an immediate family member, if they are not registered in the same household, their income cannot be used to supplement the requirement. Siblings are not considered immediate family members, and therefore cannot supplement the income requirement. * (Reference) As of 2025, the required minimum annual pre-tax income of the sponsor (for the past year) must be at least the amount listed below: Household Size 2 persons 3 persons 4 persons 5 persons 6 persons 7 persons Required Income (KRW) 23,595,948 30,152,118 36,586,638 42,649,152 48,388,830 53,930,568 * For households with 8 or more members, the income requirement increases by 5,541,738 KRW for each additional person. 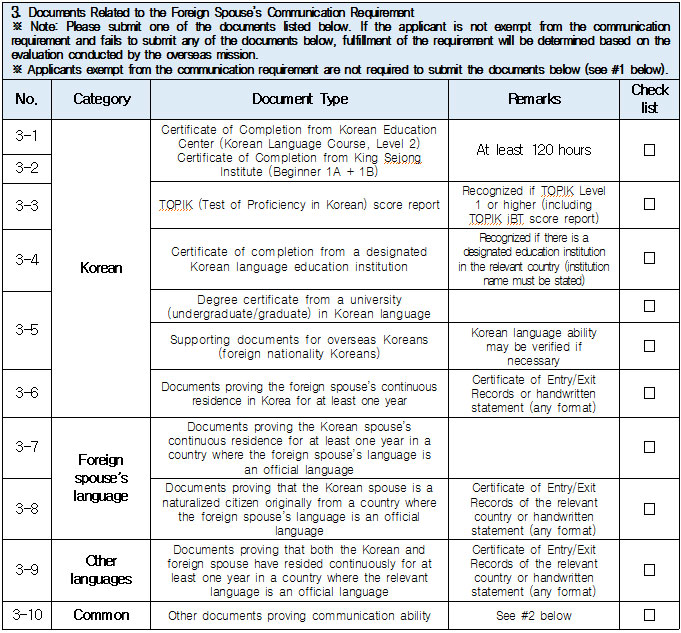 * #1 (Exemption from Communication Requirement) The submission of documents related to communication ability is exempted in the following cases: ① When the couple has a child born between them; ② When the foreign spouse has previously stayed in Korea under a Marriage Migrant (F-6) visa, regardless of the length of stay (however, this does not apply if the spouse has changed or if the same marriage was previously dissolved). * #2 (Other Documents Proving Communication Ability) If either the Korean spouse or the foreign spouse ① submits a language proficiency test score above a certain level, or ② passes an interview conducted in the relevant language at the embassy, they may be recognized as having satisfied the communication requirement. * Income requirement for households of eight or more: increases by 5,541,738 KRW for each additional household member. 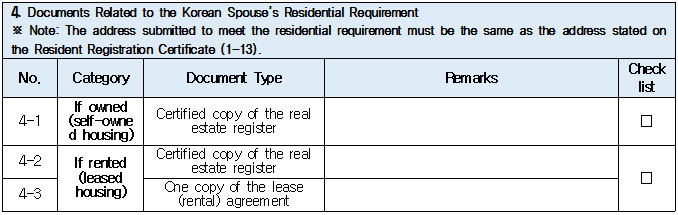 * #1 (Housing Requirement) The residence submitted to meet the housing requirement must be owned or leased under the name of the Korean spouse, or under the name of the Korean spouse’s immediate family member, brother, or sister. In principle, if the residence is owned or leased under the name of a third party, it is considered not to meet the housing requirement. However, exceptions may be granted in cases deemed acceptable under social norms, such as company-provided housing. 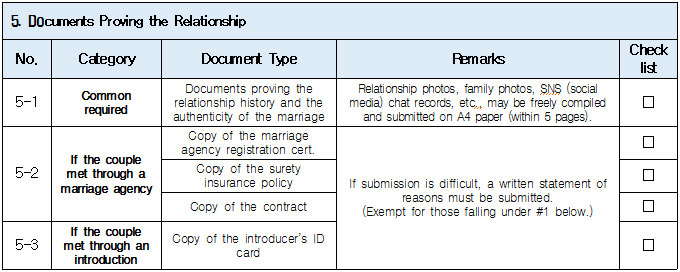 * #1 (Exemption from Submission of Documents Explaining How the Couple Met) ① When the couple has a child born between them; ② When the foreign spouse has previously stayed in Korea under a Marriage Migrant (F-6) visa, regardless of the length of stay (however, this does not apply if the spouse has changed or if the same marriage was previously dissolved). [List of Required Documents for Simplified Submission by Case] ▢ In the case where the couple has a child born between them – Required Documents List 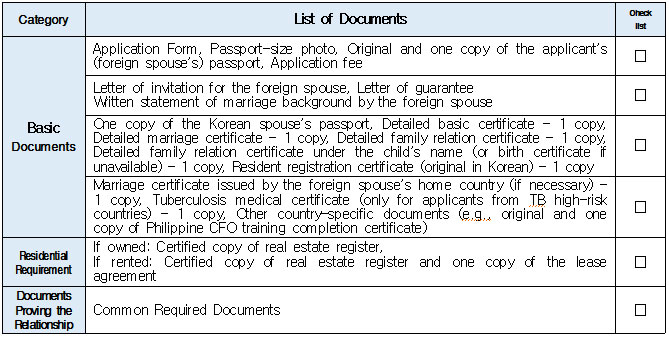 ▢ List of Required Documents for Those Fully Exempt from Submitting the Korean and Foreign Spouses’ Medical Examination Certificates and Criminal Record Certificates 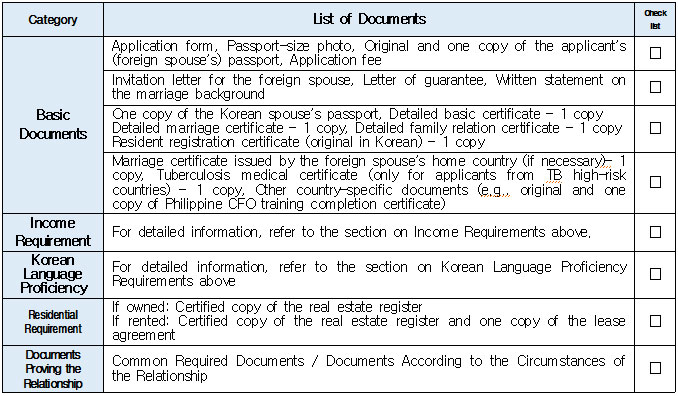 ▢ In the case where the foreign spouse has previously stayed in Korea under a Marriage Migrant (F-6) visa, regardless of the length of stay 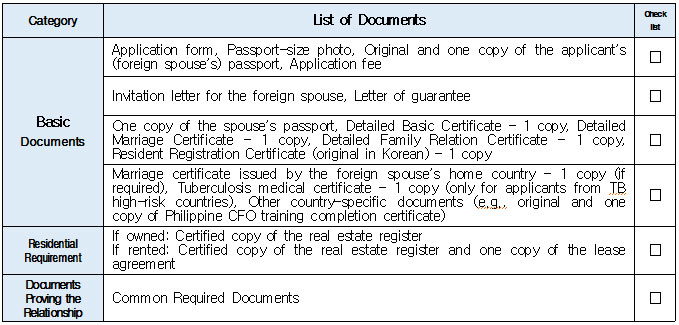 |
| Extension of Stay Permission (F-6-1) | (1) Title
Extension of Stay Permission (F-6-1) (2) Content 1. Extension of Stay Permission for Spouses of Korean Nationals (F-6-1)** A. First-Time Extension of Stay * After entering Korea with a Marriage Migrant Visa (F-6-1, 90 days), the foreign spouse must apply for an extension of stay and foreigner registration at the immigration office (district office or branch) having jurisdiction over their residence within 90 days. * Duration of stay granted : 1 year from the date of entry. * Exception : For nationals of the 7 countries subject to the international marriage guidance program designated by the Minister of Justice: * If the early adaptation program is completed: 2 years granted at the time of foreigner registration * If not completed: Granted in 6-month increments up to 2 years from the date of entry * Countries : China, Vietnam, Philippines, Thailand, Cambodia, Uzbekistan, Mongolia Required Documents : 1. Application Form (Form No. 34), passport, one standard-sized ID photo, application fee 2. Detailed Marriage Certificate and Resident Registration Certificate of the Korean spouse * If a child was born between the couple: Child’s Family Relation Certificate 3. Foreigner’s Job Report 4. Proof of residence (e.g. lease agreement, housing provision certificate, stay expiration notice, utility payment receipt, dormitory fee receipt, etc.) B. Subsequent Extension of Stay Eligible Applicants : * Individuals currently residing with the **F-6-1 status Duration of stay : * Up to 1 year * **Up to 3 years** if the applicant is raising a child born with the Korean spouse Required Documents : 1. Application Form (Form No. 34), passport, application fee 2. Detailed Marriage Certificate 3. Resident Registration Certificate 4. If there is a child: Child’s Family Relation Certificate 5. Foreigner’s Job Report 6. Proof of residence 7. Any other documents requested during the review process 2. Extension of Stay in Cases of Separation, Divorce Proceedings, or Missing Spouse (F-6-1) Eligible Applicants: Foreigners with F-6-1 status who meet one of the following conditions : 1. Separated from spouse * Separation means the marriage is legally intact but the couple has been living apart for an extended period. Weekend couples are not considered separated. 2. In the process of divorce litigation * Includes preparing for divorce or appealing previous decisions 3. Spouse is missing, but the court has not yet declared them legally missing Required Documents Common Documents : 1. Application (Form No. 34), passport, alien registration card, application fee 2. Detailed Marriage Certificate and Resident Registration Certificate of Korean spouse 3. Child’s Family Relation Certificate (if applicable) 4. Foreigner’s Job Report 5. Proof of residence Additional for Each Case : * Separation * Evidence proving separation: * Korean spouse’s runaway report * Medical report/photos of injuries * Admission to domestic violence shelters * Criminal court rulings * Third-party statements * Confirmation from certified women’s organizations * If spouse is incarcerated*: prison certificate, confirmation from spouse’s relatives (within 4th degree) * Divorce * Divorce litigation documents (e.g. certificate of lawsuit filing) * Missing * Documents proving spouse is missing * Court's receipt of disappearance declaration, missing person report, third-party confirmation * Others * Any other documents deemed necessary 3. Extension of Stay for Child-Raising Parent (F-6-2) A. First-Time Extension of Stay * After entering Korea on an F-6-2 (90-day) visa, the applicant must apply for extension and foreigner registration within 90 days. * Duration : * 1 year from entry (2 years if early adaptation program completed) Required Documents : 1. Application (Form No. 34), passport, one ID photo, fee 2. Child’s Basic Certificate and Family Relation Certificate (if the child is Korean) 3. Foreigner’s Job Report 4. Proof of residence B. Subsequent Extension of Stay Eligible Applicants : * Individuals residing with **F-6-2** status Duration : * Up to 3 years Required Documents : 1. Application (Form No. 34), passport, fee 2. Child’s Basic Certificate and Family Relation Certificate 3. Evidence of ongoing childcare (e.g. school fee receipts, medical bills) 4. Foreigner’s Job Report 5. Proof of residence 6. Other documents if required Special Rule : Visitation Rights Holders 1. Eligible Applicants : * Individuals with F-6-1 status whose marriage has ended, but who hold court-recognized visitation rights to a child born with the Korean spouse 2. Assessment Criteria (all must be met): * Visitation rights have not been restricted or revoked by court * Applicant is **maintaining regular contact** with the child * ➝ If visitation is revoked or contact is not maintained, stay will not be granted 3. Required Documents : * Application, child’s Basic and Family Relation Certificates, court ruling (if applicable), photos or documents proving ongoing interaction, Foreigner’s Job Report, etc. 4. Period of Stay : * Up to 1 year under F-6-2 status 4. Extension of Stay for Divorced, Widowed, or Spouse-Declared-Missing Foreigners (F-6-3) A. First-Time Extension After Spouse’s Death Eligible Applicants : * F-6-1 holders whose Korean spouse passed away during a normal marriage Required Documents : 1. Application (Form No. 34), passport, alien registration card, fee 2. Proof of death (e.g. death certificate, basic certificate) 3. Marriage Certificate and Child’s Family Certificate (if applicable) 4. Foreigner’s Job Report 5. Proof of residence 6. Other documents as needed B. First-Time Extension After Spouse Declared Missing Eligible Applicants : * F-6-1 holders whose Korean spouse is missing under *Civil Act Article 27, and has been legally declared missing by the family court Required Documents : 1. Application (Form No. 34), passport, alien registration card, fee 2. Court-issued **Declaration of Disappearance** 3. Marriage Certificate 4. Child’s Family Certificate (if applicable) 5. Foreigner’s Job Report 6. Proof of residence 7. Other documents if required C. First-Time Extension After Divorce (No Fault of the Foreigner) Eligible Applicants : * F-6-1 holders who were divorced due to reasons not their fault (e.g. spouse’s abandonment, abuse) Required Documents : 1. Application (Form No. 34), passport, alien registration card, fee 2. Detailed Marriage Certificate indicating divorce 3. Divorce-related litigation documents (court ruling, mediation, etc.) 4. Proof that divorce was not the foreigner's fault: * Spouse’s runaway report, abuse-related medical records, non-prosecution document, women's organization confirmation, affidavit from spouse's relative, community leader confirmation 5. Child’s Family Certificate (if applicable) 6. Foreigner’s Job Report 7. Proof of residence 8. Other necessary documents **Special Note**: * Even if the foreigner is at fault, they may be granted F-6-3 (1-year stay) if they are supporting the Korean spouse’s family and provide documentation. D. Subsequent Extension for F-6-3 Holders Eligible Applicants : * Foreigners already residing under **F-6-3** status Required Documents : 1. Application (Form No. 34), passport, alien registration card, fee 2. Child’s Family Certificate (if applicable) 3. Foreigner’s Job Report 4. Proof of residence 5. Other documents as necessary 5. Extension of Stay for Household Affairs (F-1-6) A. Eligible Applicants * Foreigners whose marriage has ended but do not qualify for F-6-3, yet must remain in Korea due to matters such as property division or estate settlement B. Assessment Criteria * Whether the marriage was maintained normally before the breakup * Whether remaining in Korea is unavoidable C. Duration of Stay : * Up to 6 months per extension * Valid up to 1 year from status change * Exception : If involved in ongoing civil suits |
| Re-entry Permit | (1) Title
Re-entry Permit (2) Content 1. Re-entry Permit Exemption Who is exempt : * A person who holds Marriage Migrant status (F-6, including former F-2-1 and F-2-10) and is a registered foreign resident, intending to re-enter Korea within 1 year from the date of departure. Exemption period : * 1 year Note : If the person’s remaining period of stay is less than 1 year, the exemption applies only within the period of stay. 2. Multiple Re-entry Permit Eligible applicants : * A person who holds **Marriage Migrant status (F-6, including former F-2-1 and F-2-10)** and is a registered foreign resident, intending to **re-enter Korea after more than 1 year but within 2 years** from the date of departure. Permit duration : * Up to 2 years Note: If the remaining period of stay is **less than 2 years, the permit will be granted only within that remaining period. Fee : * A processing fee applies (amount not specified here). Important: Individuals who are subject to entry restrictions must receive approval from the Immigration Headquarters for the re-entry permit. |
| Foreigner Registration | 1. Spouse of a Korean National (F-6-1)
A person who enters Korea on a Marriage Migrant visa (F-6-1) must register as a foreigner at the immigration office (main office or branch) within 90 days of entry based on their place of residence. Required Documents : ① Application form (Form No. 34), passport, one standard-sized photo, and fee ② Korean spouse’s detailed Certificate of Marriage ③ Korean spouse’s Resident Registration Certificate ④ If the couple has children: Family Relation Certificate under the child's name 2. Child Caregiver (F-6-2) Eligible applicants : * Individuals who entered Korea on a Child Custody visa (F-6-2) Additional screening criteria and notes : * If registration is done after 90 days from the date of entry, the person will be subject to legal penalties. Period of stay granted : * 1 year from the date of entry Required Documents : ① Application form (Form No. 34), passport, one standard-sized photo, and fee ② If the child is a Korean citizen: Basic Certificate and Family Relation Certificate under the child’s name ③ Document proving the place of residence |