Chapter 19 The Four Types of Social Security
- Section 4: National Health Insurance
-
I. Concept
1. Purpose
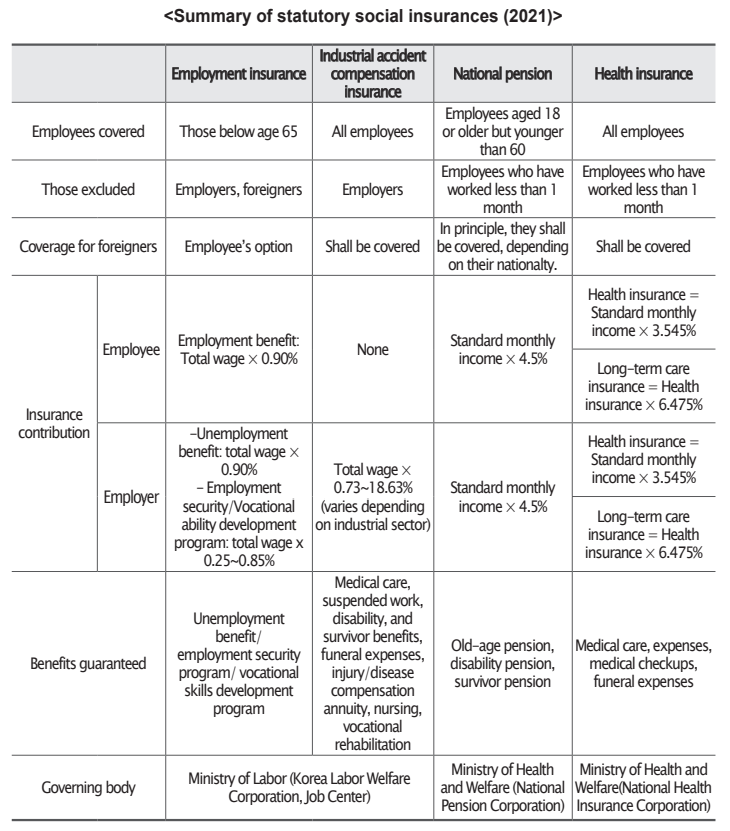
National Health Insurance aims to improve public health and social security by providing insurance benefits for the prevention, diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation of injured and ill people, as well as assist with costs of childbirth and death, and promote health(Article 1 of the National Health Insurance Act, or NHIA). National Health Insurance is a compulsory insurance that is divided into workplace and regional insurers. Currently, it covers about 97% of all citizens, with other medical services covered under the Medical Benefits Act, which is a form of public assistance for beneficiaries of the Basic Livelihood Subsidy.26) The self-employed who do not employ workers, daily workers employed for less than one month, and part-time workers who work less than 60 hours a month are not required to subscribe.27)
2. Scope of application for working places
The National Health Insurance Plan is applicable to workers at all companies.
3. Workers excluded from corporate insurance coverage
- Daily workers who are hired for less than one month
- Workers or employees working at seasonal or temporary work places
- Irregular workers or part-timers(whose working hours are less than 60 hours per month) who do not attend the work place regularly.
4. Employer’s major duties
① Application report of workplace
Within 14 days after it becomes mandatory for the company to apply
② Report any changes at the workplace
When there is a change in the employer, category of business, name, location, telephone number, etc.
③ Acquisition(change) and loss report of the insured or his/her dependents
④ Retrieval and return of health insurance card when no longer eligible(retirement or severance)
⑤ Report wages and change of standard monthly wage for the insured
- Report total wages paid last year by the end of February each year
- Report total wages of an employee with whom the employment relationship has ended
- Report any changes in the standard monthly wage
⑥ Deduction and payment of the premium
- Premiums are deducted from the wages of the insured
- Payment on the 10th of the following month for the present month
⑦ Measures necessary to check health for the insured and his/her dependents, and report the medical analysis results from the health examination center
⑧ Keep documents concerning health insurance for 3 years for each employee; health checkup reports for 5 years
II. Insurance Premiums
1. Premium rate
The insurance premiums for subscribing workers are an amount calculated by multiplying the standard monthly salary by the premium rate, with 50% of the premiums borne by workers and 50% by employers(Article 69). Therefore, the premiums are paid according to the individual’s standard monthly salary.28) The standard monthly wage refers to the total monthly wage that the insured receives at the workplace each month. Monthly wage is graded within a range of a given amount, and the standard amount of each grade is then used to calculate the premium by multiplying the premium rate.
2. Premium calculation
The standard monthly wage of the current year calculated based upon the previous year’s premium adjustment serves as the basic data for the premium charge. Thus, the actual standard monthly wage of the current year must be calculated after the end of the fiscal year to determine the premium for the next year.
III. Insurance Benefits
1. Medical treatment benefits
Medical treatment benefits include prevention, diagnosis, treatment and rehabilitation for the insured and his/her dependents, childbirth, and death, and direct medical service(material or cash benefits) for health examinations.
2. Medical treatment expenses
(1) Childbirth expenses
If the insured(or dependent) gives birth at a place other than a medical institute(in cases of stillbirth, 16-week pregnancy), an estimated amount of medical expenses shall be paid.
(2) Medical expenses
If the insured(or dependent) is unable to use a certified medical center and instead uses a facility under operational suspension or an unverified medical institute, an estimated amount of the medical expenses shall be paid regardless.
3. Health examination
At least one health examination every two years shall be given to diagnose disease at its premature stage(for non-office workers, once a year).
4. Support with private charges
If the insured(or dependent) pays more than 2 million won per 6 month-period for medical treatment at a medical center, the corporation shall bear the exceeded amount, to help reduce the personal financial burden of the heavy medical expenses.
5. Assistive devices for the handicapped
If the insured(or dependent) who is registered as a disabled person under Article 32 of the Disabled Welfare Act and purchases an assistive device, then a partial reimbursement of the purchase shall be provided. If the price is under the criteria amount for the help-aid device, 80% of the actual expenses(including VAT) shall be reimbursed.
6. Refund of individual burden
If the insured(or dependent) receives treatment and pays over the amount of his/her legal individual burden, the exceeded amount shall be reimbursed.
IV. Long-term Care Insurance
1. Concept
Long-term care insurance is a social insurance system separate from National Health Insurance. It was introduced in July 2008 due to aging of the population and the necessity to care for the elderly. It provides essential care services such as face washing, bathing, meals, assistance with using the toilet, and nursing care for elderly persons unable to move alone due to age-related diseases such as dementia and stroke.29)
2. Categories of long-term care
- Category 1: Incapable of activities for daily living and getting in and out of bed; requires full assistance in all daily activities; those who show problem behavior almost every day with reduced judgment. Examples would be those who stay in bed almost all day, or who cannot eat without assistance.
- Category 2: Requires considerable assistance with basic activities such as eating and dressing; those who frequently exhibit problematic behavior with reduced judgment. Examples would be those who can sit or move within their rooms without assistance.
- Category 3: Requires partial assistance for eating, dressing and bathing. Examples would be those who can move only short distance with a walker.
3. Contribution for Long-term Care Insurance
A contribution for long-term care insurance(12.95%) will be added to the premium for National Health Insurance.
Contribution for long-term care insurance = premium for National Health Insurance × Rate of contribution for long-term care insurance (12.95%).
(Employer and employee shall each pay half.)