IV. Restructuring-Related References
- Section 2. Unemployment Benefits
-
1. Employees Eligible for Unemployment Benefits
(1) Who is eligible for employment benefits?
Employment benefits are paid to unemployed persons who are satisfying the following two criteria: the employee had to leave a job involuntary for reasons such as dismissal for managerial reasons, expiration of contract period, etc. after having worked more than 180 days during the last 18–month period, and the unemployed person is actively making efforts to become reemployed. However, unemployment benefits shall not be given in cases where the employee has left his/her job to transfer to another job or become self-employed or in cases where the employee is separated from employment following the advice of the employer or dismissed due to reasons attributable to him/herself.
※ Cases dismissed due to critical reasons attributable to employee
1) In cases where he/she is sentenced to imprisonment (without being assigned prison labor or more severe punishment) for violating the Criminal Act or laws relating to employment;
2) In case he/she has, on purpose, caused a considerable hindrance to the business or inflicted any damage to property due to embezzlement, disclosure of corporate secret, damage to property, etc. and
3) In case he/she has been absent from work for a long time without due notice and justifiable reasons.
* Though the employee who falls under one of the above items resigned voluntarily by the employer’s advice, he/she shall not be eligible for recipient of unemployment benefit.
(2) Can the employee receive unemployment benefit if he/she was hired while receiving unemployment benefit?
Unemployment benefit is paid to an unemployed person when he/she reports unemployment and was recognized as an eligible recipient, and when he/she made efforts for reemployment. Therefore, this beneficiary process requires the recognition of unemployment and evidence to prove efforts for reemployment for a unit period of three to four weeks. Therefore, in principle, the reemployed employee cannot be eligible for unemployment benefit. Provided that in case an eligible recipient is employed in a job that is deemed certain to keep him/her employed for more than six months, or in cases where an eligible recipient is deemed certain to run his/her own business for six months or more, then the reemployed person can get a certain portion (1/3 ~ 2/3 of the benefit still left) as an early reemployment incentive.
(3) If the employee signed a letter of resignation, can he/she receive unemployment benefits?
In cases where the employee resigned from the company voluntarily due to reasons such as submitting a resignation letter because of a change of occupation, becoming self-employed or going back to school, unemployment benefit shall not be given in principle. However, the employee can receive unemployment benefits under the following special
Reasons for unemployment acceptable for eligible beneficiary
(Employment Insurance – Decree (Article 101 (2) – Table 2)
1. In cases where one of the following occurred for longer than two months within a one-year period prior to his/her resignation:
A. Where his/her current working conditions decreased lower than those suggested at the time of employment or those generally applied during employment, or in cases where his/her payment of wages was delayed;
B. Where his/her wages paid for contractual working hours was lower than the minimum wage under the Minimum Wage Act;
C. Where the employer violated the restriction on extended work under Article 53 of the Labor Standards Act; or
D. In cases where the allowance for business suspension was less than 70 percent of his/her average wage.
2. In cases where the company surely faces bankruptcy or cessation of business, or in cases where a massive personnel reduction is planned.
3. Under one of the following reasons, the employee was advised by the employer to voluntarily resign, or in cases where the employee resigned through the employer’s promotion campaign for voluntary resignation in accordance with personnel reduction plan.
A. Transfer, acquisition and merger of business, or partial cessation of business or change of business;
B. Change of working environment due to closing or downsizing of the organization or the introduction of new technology/technical innovation; and
C. Business deterioration, personnel redundancy or an equivalent reason.
4. In cases where it is hard to commute due to one of the following reasons:
A. When the company relocates or the employee is transferred to a far-away workplace;
B. When the employee moved to support his/her spouse or family; and
C. When it is hard to commute to the company due to unavoidable reasons.
5. In cases where the employee had to nurse his/her parents or family member who is ill for more than 30 days.
6. In cases where the employee cannot fulfill his/her duties due to deteriorating health, mental and/or physical disorder, disease, injury, loss of eyesight, hearing or sense of touch.
7. In cases where the employee cannot fulfill his/her duties continuously due to pregnancy, childbirth, or military service under ‘the Military Service Act’.
8. In cases where there is an assumption that ordinary employees might also resign from the company if they were under such similar circumstances.
2. Amount of Unemployment Benefit
(1) How much can an unemployed person receive from unemployment benefits?
The unemployment benefit is 50% of the average wage prior to separation within the range of 90 to 240 days in accordance with the age and insured period as of separation time.
à Maximum amount: 60,000won per day(As of 2018)
à Minimum amount: daily contractual working hours x 90% of daily minimum wage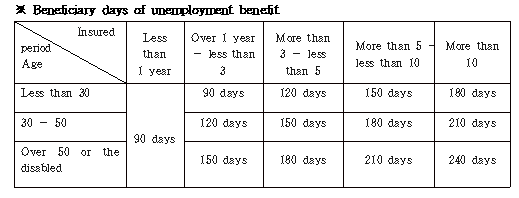
(2) Until when can the unemployed person apply for unemployment benefits?
Even though an unemployed person is eligible for unemployment benefits, he/she cannot receive unemployment benefits if 12 months has passed from the day of separation. These 12 months are called ‘period of benefit payment’. As unemployment benefits cannot be paid if the period of benefit payment expires, the unemployed person shall apply for the eligibility of benefit payment to the Employment Support Center without delay right after separation.
※ Reasons for extension of payment period (maximum extension is 4 years)
1) Injuries or diseases of the recipient (excluding injuries or diseases for which injury and disease benefits are being paid);
2) Injuries or diseases of the recipient's spouse or lineal ascendants or descendants;
3) Mandatory military service under the Military Service Act;
4) Detention or execution of sentence on criminal charges; and
5) Pregnancy, childbirth, and childcare (limited to within 3 years after birth of a child).
3. Payment Procedure of Unemployment Benefit
(1) What do you do to receive unemployment benefits?
To receive unemployment benefits, the unemployed person shall visit the Employment Support Center in his/her location with identification documents, such as a Residence Certificate or Driver’s License, immediately separation and report unemployment. The report of unemployment shall include an application for work and an application for the recognition of eligibility for benefit, and then the head of an Employment Security Office shall notify the applicant of the results of the decision within 14 days.
(2) What is the recognition of unemployment?
The recognition of unemployment means that the head of an Employment Security Office recognizes that the unemployed person has actively engaged to become reemployed during a certain recognition period of unemployment, after unemployed person received the recognition of beneficiary eligible for unemployment benefits.
An eligible recipient shall present him/herself on a date of recognition of unemployment designated by the head of an Employment Security Office over the course of an one to four week period counted from the date of reporting unemployment and report the efforts made to be reemployed, and the head of the Employment Security Office shall recognize his/her unemployment based upon reported contents. An eligible recipient cannot receive unemployed benefit if he/she could not get the recognition of unemployment because of failure to attend the Employment Security Office.
(3) What are active efforts to become reemployed?
An eligible recipient shall make active efforts to become reemployed (i.e., get a job) in accordance with the reemployment action plan completed on the first recognition day of unemployment so that he/she can get the recognition of unemployment. Here, reemployment action means the unemployed person’s reemployment activities such as submission of job applications or participations in job interviews, and/or efforts to become self-employed. Job-seeking activities also include submission of job applications by mail, fax or email, participation in job interviews with recruiters in the job fair, or attending occupation guidance programs conducted by the Employment Security Office.
4. Illegal Receiving of Unemployment Benefit
(1) What is the illegal receiving of unemployment benefits?
Unemployment benefits are payable when the unemployed person is recognized as an eligible recipient by the head of an Employment Security Office and makes efforts to be reemployed during the recognition period of unemployment. It is illegal to receive unemployment benefits through false or other fraudulent methods.
※ The most common cases of illegally receiving benefits involve a person not reporting reemployment during the recognition period of unemployment or reporting it using fraudulent information, or that he/she made a false report regarding the reason for separation or his/her wages while employed.
(2) What are the penalties for illegally receiving unemployment benefits?
If it is found that a person received unemployment benefits through illegal methods, he/she shall refund the benefit received and additionally pay the same amount equivalent to the illegally received benefit as a penalty. Further, his/her unemployment benefits will stop, and the person concerned could face criminal prosecution. If a company manager was involved in perpetuating the illegality, the employer shall also share joint responsibility with the person.
1) A small illegal benefit can be forgiven only once.
2) Criminal punishment can be pursued where a person violates the law twice, where two people or more collaborate and receive benefits illegally, and in cases where a person rejects the requests to repay the illegally received benefits despite repeated demands from the Employment Security Office.
3) In cases where illegal benefits were paid due to a falsified description on the company’s confirmation of severance, an additional fine (2 ~ 3 million Won) will be charged to the company.






